단어 정렬
| 2 초 | 256 MB | 174784 | 73233 | 54897 | 40.354% |
문제
알파벳 소문자로 이루어진 N개의 단어가 들어오면 아래와 같은 조건에 따라 정렬하는 프로그램을 작성하시오.
- 길이가 짧은 것부터
- 길이가 같으면 사전 순으로
단, 중복된 단어는 하나만 남기고 제거해야 한다.
입력
첫째 줄에 단어의 개수 N이 주어진다. (1 ≤ N ≤ 20,000) 둘째 줄부터 N개의 줄에 걸쳐 알파벳 소문자로 이루어진 단어가 한 줄에 하나씩 주어진다. 주어지는 문자열의 길이는 50을 넘지 않는다.
출력
조건에 따라 정렬하여 단어들을 출력한다.
예제 입력 1
13
but
i
wont
hesitate
no
more
no
more
it
cannot
wait
im
yours
예제 출력 1
i
im
it
no
but
more
wait
wont
yours
cannot
hesitate
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
int main(int argc, char* argv[]) {
int input_count = 0;
scanf("%d", &input_count);
char** input_string = (char**)malloc(sizeof(char*) * input_count);
char buffer[51] = { 0 }, temp[51] = { 0 };
while (getchar() != '\n'); //엔터키 잡기
for (int i = 0; i < input_count; i++) {
fgets(buffer, sizeof(buffer), stdin);
buffer[strcspn(buffer, "\n")] = '\0';
input_string[i] = (char*)malloc(sizeof(char) * 51);
strcpy(input_string[i], buffer);
fflush(stdin);
}
for (int i = 0; i < input_count - 1; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < input_count - 1 - i; j++) {
if (strlen(input_string[j]) > strlen(input_string[j + 1])) {
strcpy(temp, input_string[j + 1]);
strcpy(input_string[j + 1], input_string[j]);
strcpy(input_string[j], temp);
}
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < input_count - 1; i++) {
if (strcmp(input_string[i], input_string[i + 1]) == 0) {
free(input_string[i]);
for (int j = i; j < input_count - 1; j++) {
input_string[j] = input_string[j + 1];
}
input_count--;
i--;
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < input_count - 1; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < input_count - 1 - i; j++) {
if (strlen(input_string[j]) == strlen(input_string[j + 1])) {
if (strcmp(input_string[j], input_string[j + 1]) > 0) {
strcpy(temp, input_string[j + 1]);
strcpy(input_string[j + 1], input_string[j]);
strcpy(input_string[j], temp);
}
}
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < input_count; i++) {
printf("%s\n", input_string[i]);
}
for (int i = 0; i < input_count; i++)
free(input_string[i]);
free(input_string);
return 0;
}
본래 작성한 코드로, 로직 흐름을 보면
1. 입력한 "입력 수"에 따라 최대 문자 길이 '50'에 null값까지 포함한 51 byte의 크기를 가지는 배열 생성.
-> 공간 비효율적
2. 문자열 길이대로 bubble 정렬, 이후에 사전순 bubble 정렬
-> 시간 복잡도가 O(n^2) + O(n^2)으로 매우 비효율적
3. 2중 for문 내에서 strcpy를 3번이나 호출함
-> 매우매우 비효율적
4. 공간이 넉넉하다면, 굳이 겹치는 원소를 free해줄 필요가 없다. 불필요한 쓰기 행위일 수 있음
-> 이전 원소와 비교하여 같지 않은 원소만 출력하는 방향으로 수정할 수 있다.
결과 :

매우 비효율적인 프로그램으로 시간 초과 오답이다.
해당 문제의 정답 코드를 보면,
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
int cmp(string a, string b) {
// 1. 길이가 같다면, 사전순으로
if (a.length() == b.length()) {
return a < b;
}
// 2. 길이가 다르다면, 짧은 순으로
else {
return a.length() < b.length();
}
}
// 범위가 크기때문에 전역변수로 설정
string word[20000];
int main() {
int main() {
int N;
cin >> N;
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
cin >> word[i];
}
sort(word, word + N, cmp);
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
// 중복된 경우 한번만 출력
if (word[i] == word[i - 1]) {
continue;
}
cout << word[i] << "\n";
}
return 0;
}
C++의 standard library를 사용하여 간단하게 풀 수 있다.
이러한 문제를 "STL 코딩" 문제라 부르며, Standard Library를 잘 활용하는 능력을 확인한다.
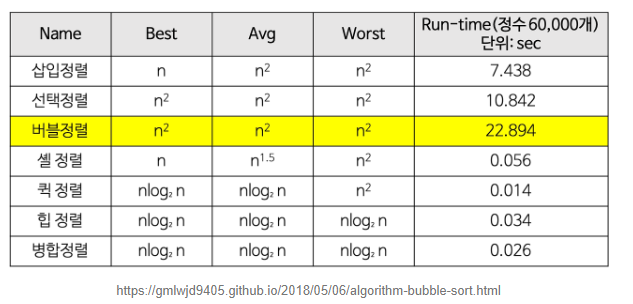
버블정렬은 비효율적이며, 힙 퀵 병합 정렬을 사용하면 시간이 줄어들것이라 예상할 수 있다.
C로 풀고싶지만 stl로 출제 의도를 생각하고 넘어가겠다..
'알고리즘 > 백준' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [백준] 1929 소수 구하기 (0) | 2024.02.22 |
|---|---|
| [백준] 1920 수 찾기 (0) | 2024.02.19 |
| [백준] 1676 팩토리얼 0의 개수 (0) | 2024.02.17 |
| [백준] 1654 랜선 자르기 (0) | 2024.02.16 |
| [백준] 1018 체스판 다시 칠하기 (4) | 2024.01.03 |